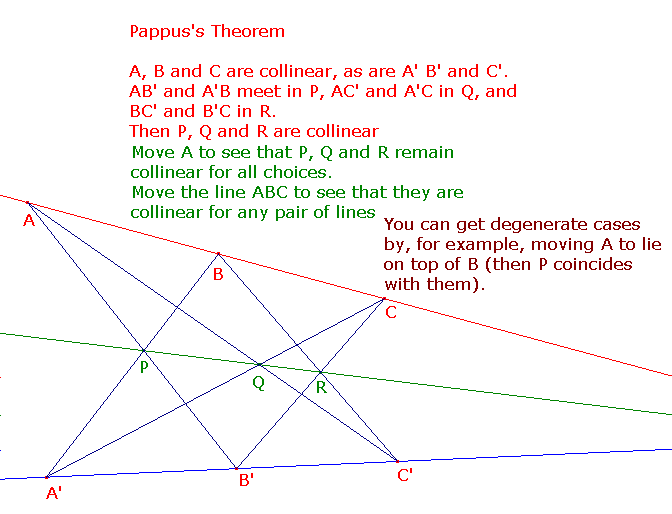
To allow us to apply duality,
Pappus's Theorem may be restated as
If alternate vertices of a hexagon are
collinear,
then the intersections of
opposite sides are collinear.
The dual is then
If alternate sides of a hexagon are
concurrent,
then the lines joining opposite vertices are concurrent.
which is Brianchon's First Theorem.
Download pappus.fig